Cell Structure
Table of Contents
Organelles
- Little organs that carry out specialized functions.
- Cellular machinery.
Prokaryotic organelles
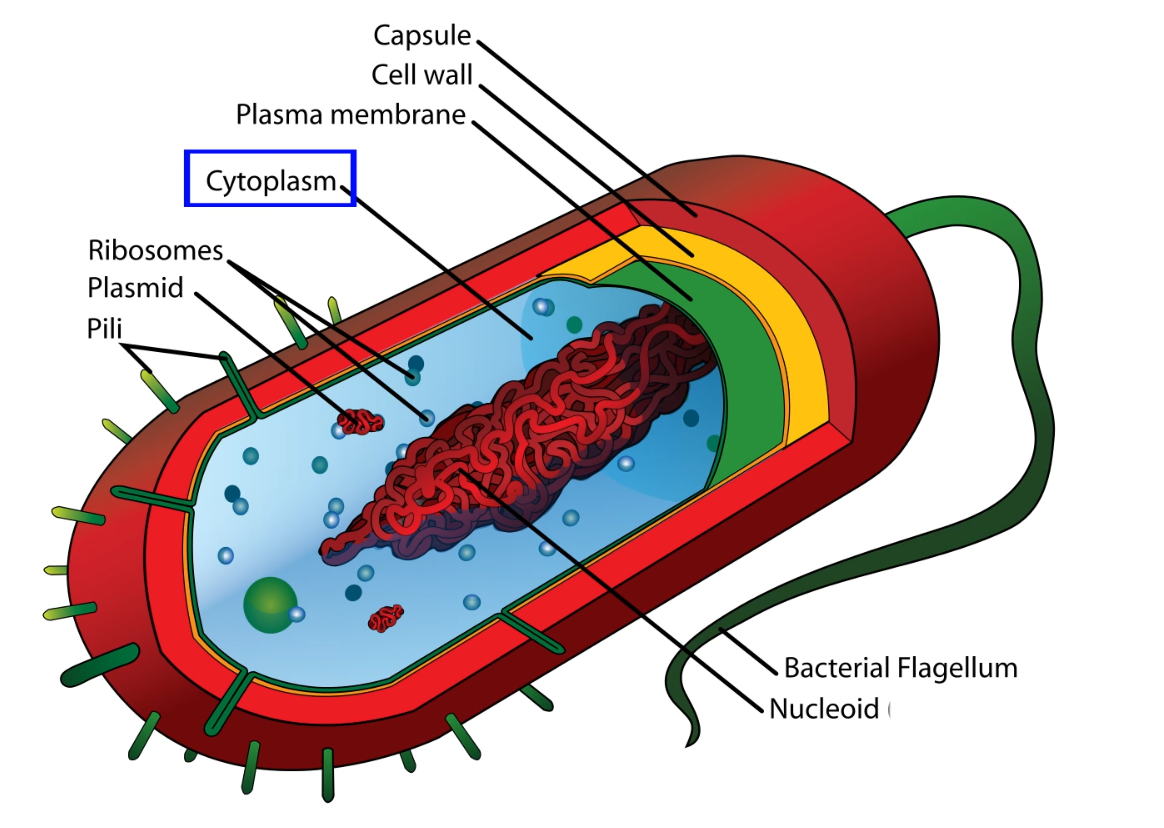
- Also called no membrane-bound organelles.
- These are organelles that are not inside of a membrane of a cell.
Plasma/Cell Membrane
- It seperates what's inside and outside of the cell.
- They let some things through such as food and energy, but also defends itself from the environment and other cells.
- It is made of phospholipid bilayer and the different types of proteins floating around it.
- The cell membrane is semi-permeable.
Phospholipids
- class of lipids that are major component of all cell membranes.
Cell Wall
- Outer layer of Plasma/Cell Membrane.
- Made up of peptidoglycan, a polymer of sugars and amino acids that creates a mesh-like layer around the cell.
- Its function is to provide additional protection for the cell.
Plants
- It is in the cellulous.
Fungi
- contain chitin.
Capsule
- The outermost layer of the cell that provides the cover for the cell wall.
Cytoplasm
- The interior of the cell is called the Cytoplasm.
- Specifically, the fluid within the membrane is called cytosol.
- Its a jelly-like fluid where all inside components are floating around.
Components
- Cytosol
- Interconnected filaments & fibers.
- storage substances.
Nucleoid
- Similar to the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell, this holds genetic information about the cell.
- The Ribosome is responsible for the DNA transcription to happen.
Plasmid
- A small, extrachromosomal DNA that is physicall seperated from the cell's DNA.
- It can replicate independently and is also vital for the survival of a cell or organism.
Ribosomes
- Sites of protein synthesis.
- They are responsible for protein production as a product of DNA transcription.
- It does this by binding itself to mRNA (messenger RNA) to determine the correct sequence of amino acids.
- The DNA translation provides the protein (that includes enzymes from the DNA) and DNA polymerase.
- The process also provides hexokinase which has a role in metabolism that provides the energy needed for the cell to function.
- You can compare this to mitochondria in the eukaryotic cells.
Flagellum
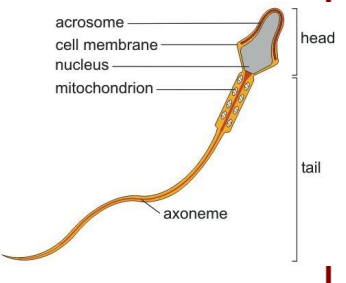
- Plural-form Flagella.
- Whip-like extensions that allows a cell to move.
- Found on sperm cells.
- plenty of mitochondria.
- A hairlike appendage that has a couple of functions for motility.
- The bacteria uses their flagella to:
- move in fluid (motility),
- in response to changes in concentration of chemical (chemotaxis)
- movement in response to light (phototaxis) or movement in response to oxygen levels (aerotaxis)
- helps in colonizing and infecting host organisms.
Types
- Bacterial flagella
- Archaeal flagella
Cilia
- Latin word for "eyelashes".
- tiny hairs on the surface of certain cells.
- move in a rhythmic, sweeping motion and serve to move particles or cells in your body.
- cilia lining in respiratory tract.
- Tracheal cells
- Beat and drive air impurities or foreign particles and mucus up the trachea to the mouth
- Short
- Used to move substances outside human cells.
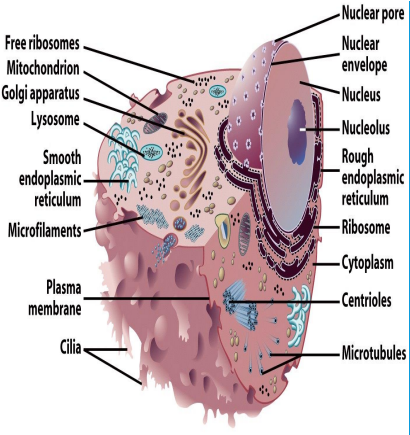
Eukaryotic organelles
Interior Structures
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- also called ER.
- network of interconnected membranes.
- it helps move substances within cells.
- Types
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
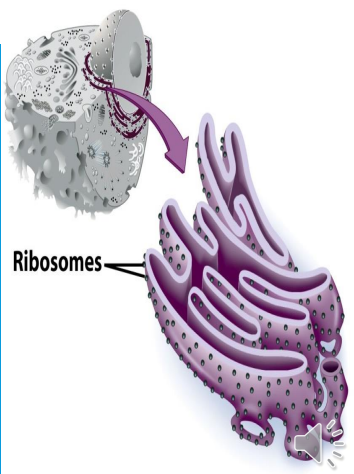
- Ribosomes attached to surface
- Manufacture proteins
- Ribosomes not permanently attached to Rough ER
- May modify proteins from ribosomes
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- No attached ribosomes
- Has enzymes that help build molecules
- Contains Lipids
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
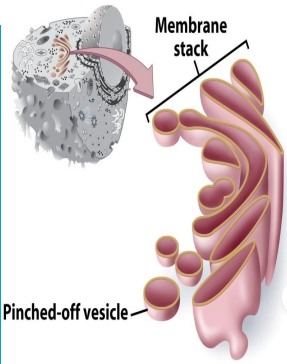
- Sorts proteins made by the ribosomes and sends them to needed places in the cell.
- "the cell's post office"
- Packaging & shipping station of cell.
Lysosomes
- organelles that are filled with digestive enzymes to remove waste and invading bacteria.
- Cell's suicide bags.
Vacuoles
- fluid filled organelles enclosed by a membrane.
- Membrane bound storage sacs
- Store materials such as food, sugar, water, and waste products
- More common in plants than animals.
Mitochondria
- "powerhouse" of the cell.
- release energy for the cell.
- converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP for the cell.
- bound by double membrane.
Chloroplasts
- Primary organelles for
Photosynthesis - chlorophyll
- captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis.
- Solar energy capturing organelle
- absorbs all other colors except green.
- Photosynthesis
- Used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy
- Energy Transformation
- Takes place in the chloroplast.
- Makes cellular food called glucose.
Cytoskeleton
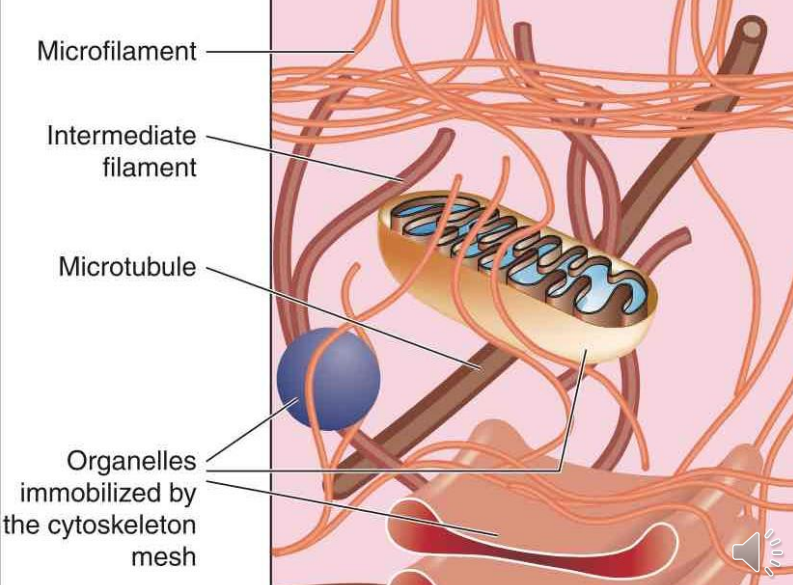
- network of protein filaments, fibers and tubules.
- Functions
- mechanical support
- anchor organelles
- it helps in moving substances
- Composition
- Microfilaments
- thinnest
- composed of the protein actin.
- Microtubules
- composed of protein tubulin
- It is involved in nucleic and cell division, organization of intracellular structure, and intracellular transport, as well as ciliary and flagellar motility
- Intermediate filaments
- maintain cell shape and help bind some cells together.
- Microfilaments
Comparison of Structure
| Bacterium | Animal | Plant | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior Structures | |||
| Cell Wall | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Plasma Membrane | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Flagella (cilla) | – | ✗ | [1] |
| Interior Structure | |||
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | ✗ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Microtubules | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Centrioles | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Golgi Apparatus | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Nucleus | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Mitochondria | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Chloroplasts | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Chromosomes | [2] | [3] | [3] |
| Ribosomes | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Lysosomes | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Vacuoles | ✗ | ✗ or – | [4] |
- [1] Sperm of a few species possess flagella.
- [2] A single circle of naked DNA.
- [3] Multiple units, DNA associated with protein.
- [4] Usually a large single vacuole in a mature cell.
References
Cells
Prokaryotic cells
- Cell Modifications and Adaptations
- Interior Structures
- Prokaryotic cells
- Prokaryotes
- Eukaryotes
- Similarities
- Nucleolus
- Nucleoid
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Interior Structures
- Compartmentalization
- Prokaryotes
- Similarities
- Centrosome
- Cytoplasm
- Sclerenchyma
- Interior Structures
- Eukaryotes
- Similarities
- Cell Wall
- Interior Structures