Vector
Table of Contents
Definition
- a quantity described by magnitude and direction
- it originated from the word "vehere" meaning to carry.
- Examples include:
- velocity
- displacement
- force
- momentum
- electric
- and
- magnetic
- fields.
- An arrow represents a vector quantity.
- The length of the arrow is scaled to be proportional to the magnitude of the vector quantity it represents; the direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the vector quantity.
- The symbol for a vector quantity is a capital letter in boldface or by placing an arrow over the symbol.
- \(A\ or \vec{A}\)
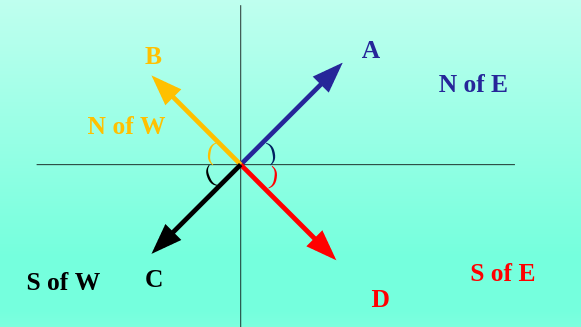
- There are several ways to specify direction of a vector. But to avoid confusion, we shall use one method throughout this session. The direction of a vector is the acute angle it makes with the east-west line.
- The angle starts for x-axis. Something like this:
Addition
- The sum of two or more vectors is called the resultant vector.
- Vectors may be added graphically or analytically.
Orthogonal Vectors
- if the angle between two vectors is \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or \(90^{\circ}\), the vectors are orthogonal.
\(a\cdot b = 0\) because \(cos(\frac{\pi}{2}) = 0\)
Unit Vector
Formula
\begin{align*}
U = \frac{v}{\lVert v \rVert}
\end{align*}
Example
Given that we have: \(V = \langle 4, -3 \rangle\): Find the unit vector of it:
\begin{align*} & U = \frac{V}{\lVert v \rVert} = \frac{\langle4, -3\rangle}{5} = \left\langle \frac{4}{5}, \frac{-3}{5} \right\rangle \\ & \lVert v \rVert = \sqrt{4^2 + (-3)^2} = \sqrt{16 + 9} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \end{align*}