Epithelial Tissues
Table of Contents
Definition
- Tightly-joined closely-packed cells
- Covers the outside of the body and lines the internal organs and cavities.
- Barrier against mechanical injury, invasive microorganisms, and fluid loss.
Found in different areas
- Body coverings
- Body linings
- Glandular tissue
Functions
- Provides surface for absorption, excretion and transport of molecules.
Main functions:
- Protection
- Absorption
- Filtration
- Secretion
Classification
Number of Layers
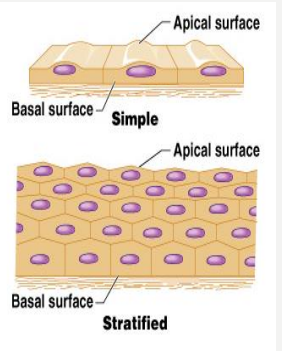
Simple
- one layer
Stratified
- more than one layer
Shape of Cells
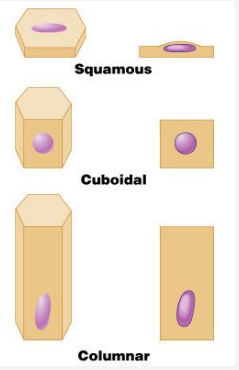
Squamous
- flattened
Cuboidal
- cube-shaped
Columnar
- column-like
Simple Cuboidal
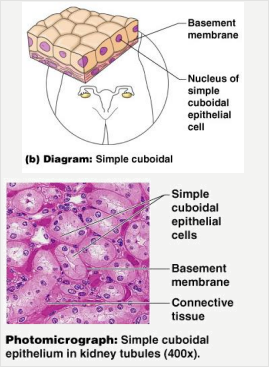
- For secretion
- Single layer of cube-like cells
- Common in glands and their ducts
- Forms walls of kidney tubules
- Covers the ovaries.
Simple Columnar
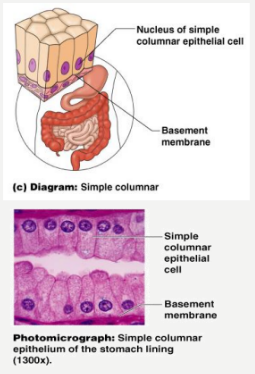
- brick-shaped cells
- For secretion and active absorption
- Single layer of tall cells
- Often includes goblet cells, which produce mucus
- Lines digestive tract
Simple Squamous
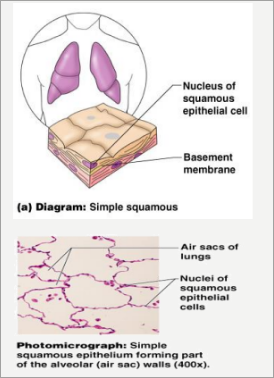
- plate-like cells
- for exchange of material through diffusion.
- Single layer of flat cells
- Usually forms membrane.
- Lines body cavities
- Lines lungs and capillaries
Stratified Squamous
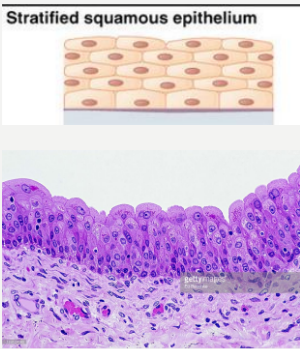
- lines the esophagus, mouth and vagina.
- Protects against abrasion.
Stratified Cuboidal
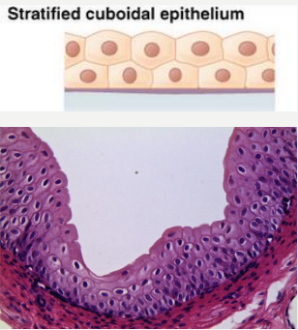
- multiple layers of cuboidal cells
- sweat glands, salivary glands, mammary glands
- found in ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules of the testes
- protective tissue
Stratified Columnar
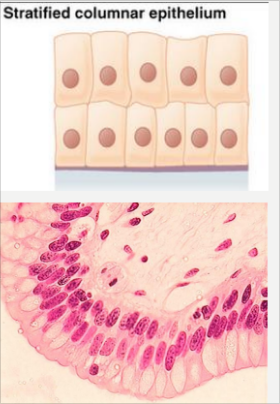
- multiple layers of columnar cells
- Found in:
- conjunctiva of the eye
- in parts of the pharynx
- anus
- the uterus
- male urethra
- vas deferens
Pseudo-stratified Columnar
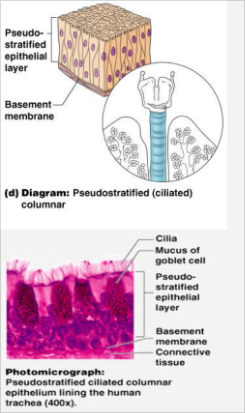
- single layer of cells
- for lining of respiratory tract
- usually lined with cilia (i.e., a type of cell modification that sweeps the mucus).
– Single layer, but some cells are shorter than others – Often looks like a double cell layer – Sometimes ciliated, such as in the respiratory tract – May function in absorption or secretion.